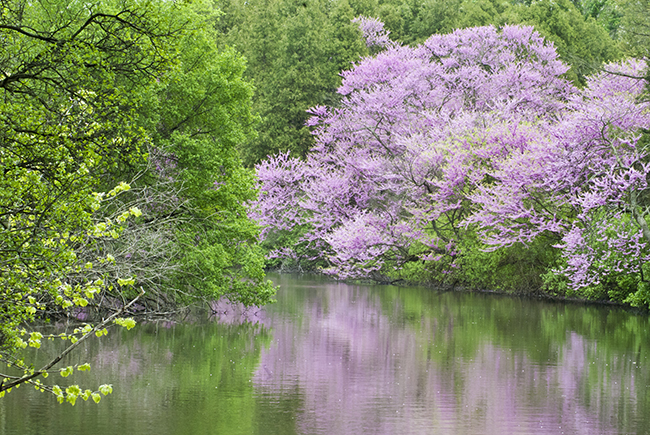
Eastern Redbud trees add a beautiful early spring glow whether a commercial parking lot or your Chicagoland backyard!
Our series on the native trees of the Chicago area is back this month with a closer look at the eastern redbud tree. Eastern redbud trees (Cercis canadensis) are small trees mostly found in the eastern half of the United States from southern Michigan and northern Illinois down to Florida and from Virginia and North Carolina west to Kansas, Oklahoma, and Texas. These trees are mostly planted for ornamental purposes as their smaller size and showy purplish-pink flowers make them easy to work into a landscape design.
The eastern redbud tree, also known in some areas as the spicewood tree, has a long history in North America. To Native American tribes, it was a source of food as they ate the flowers of the redbud and roasted its seeds. It is believed that the eastern redbud was first cultivated in 1641 and even George Washington is said to have planted eastern redbuds in his gardens at Mount Vernon. To this day, people in areas of Appalachia use the green twigs from eastern redbuds to season wild game. While the eastern redbud is no longer depended on as a source of food, it is still widely planted as an ornamental plant.
In this guide, we will discuss the main characteristics of eastern redbud trees, their biggest natural threats, and care tips to help you provide excellent care for your eastern redbuds. Your eastern redbud trees can live for up to 25 years with the proper care. At Hendricksen Tree Care, we provide professional tree care and maintenance services to help care for your trees, including eastern redbuds. Our arborists are ISA certified and can provide tree trimming and fertilization as well as diagnose and treat diseases and insect infestations.
Characteristics of Eastern Redbud Trees
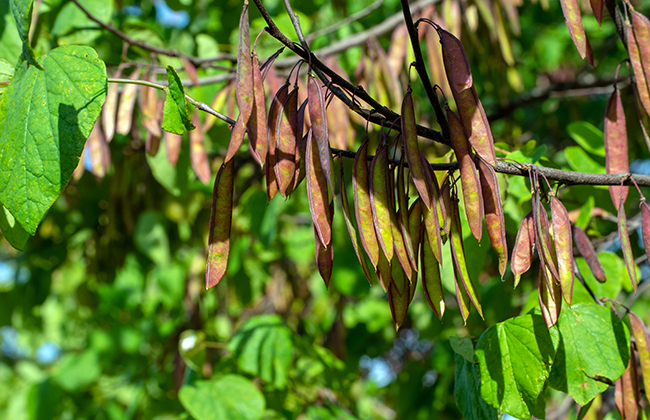

The seed pods of the Eastern Redbud tree generally ripen into autumn
Eastern redbud trees are most known for their bright, showy flowers which are shades red, purple, and pink. It is from its flowers that the eastern redbud gets its name. These trees are relatively small in size as they are typically 20 to 30 feet in height and have a width of 15 to 35 feet when full grown. Their bright flowers make them a desirable ornamental tree.
The following are the main characteristics of eastern redbud trees:
- Height: As mentioned above, eastern redbuds tend to be about 20 to 30 feet in height and 15 to 35 feet wide. These trees grow 7 to 10 feet every five to six years which means that it takes 10 to 15 years for them to reach their full height.
- Leaves: The leaves of an eastern redbud are alternate and broadly heart shaped. They are about 3 to 5 inches long and wide and are typically dark green in color in the spring and summer. In the fall, the leaves turn yellow.
- Flowers: The flowers are the signature characteristic of the eastern redbud. They appear early in the spring in March and April in clusters of 4-8 flowers. They are typically pink or purple in color and they stay in bloom for 2-3 weeks after they appear. The flowers are replaced by seed pods (legumes) by mid-summer that remain until the winter.
- Fruits: As the flowers of the eastern redbud disappear during the summer, oblong legume seed pods that are reddish brown in color take their place. The legumes ripen in October and can last through the winter.
- Bark: The bark of an eastern redbud is reddish brown in color, and it appears scaly with deep fissures. New branches are brown in color and then become darker.
- Trunk: Eastern redbud trunks tend to be twisted with spreading branches. The twigs are slender and grow in zigzag patterns.
Natural Threats to Eastern Redbuds in Illinois
Healthy eastern redbuds are great ornamental trees that can add vibrant color to your landscape. However, there are several diseases and pests that can damage your eastern redbuds and even result in the death of the tree. The following are the main pests and diseases that can affect eastern redbuds:
Diseases
- Leaf anthracnose: Leaf anthracnose is a fungal disease that causes dark, circular shaped spots to appear on the leaves. These spots will grow larger in time and they can cause the leaves to die and fall prematurely.
- Botryosphaeria canker: Botryosphaeria canker is a fungal disease that causes lesions to appear on stems, twigs, and the trunk. This disease disrupts the flow of water and nutrients throughout the tree which can cause wilting of the leaves and dying of the branches. It is possible for botryosphaeria canker to kill eastern redbuds if left untreated. A well-watered tree is less susceptible to this disease.
- Verticillium wilt: Verticillium wilt is another fungal disease that attacks the vascular system of the tree. The fungus lives in the soil and invades through the roots and it disrupts the flow of water and nutrients. Trees affected by this disease will have dark streaks on the wood below the bark and they may suffer wilting and dying of the leaves as well as branch dieback. Verticillium wilt is often fatal to affected trees.
Insects
- Red-humped caterpillar: The red humped caterpillar is about 1.5 inches long and it has a red head and white and red striped, yellow body. These caterpillars eat the leaves of eastern redbuds and lay eggs on the leaves. The health of the tree is usually not in danger from these pests as they appear right before the leaves start falling off in the fall. You can control red-humped caterpillar infestations by pruning the affected branches.
- Tent caterpillar: Tent caterpillars are reddish brown in color with blue spots and white and orange hairs. They eat the leaves of eastern redbuds and make silk webbed nests under the leaves. It is possible for tent caterpillars to defoliate eastern redbuds. Pruning the affected limbs can help control these pests.
- Scale insects: Scale insects are small insects that feed on the juices from the leaves of eastern redbuds and excrete honeydew. These insects can cause damage to the affected leaves and the honeydew excretions attract more pests. A scale infestation can be treated with horticultural oils.
- Black twig borer: The black twig borer is a small, dark colored scolytid beetle that bores into ornamental trees like eastern redbuds to overwinter and lay its eggs. When the females enter the tree to lay eggs, they bore into the wood to create galleries and line the galleries with a white fungus that feeds its young. This fungus disrupts to flow of water through the tree which causes leaves and branches to wilt and die.
Eastern Redbud Care Tips
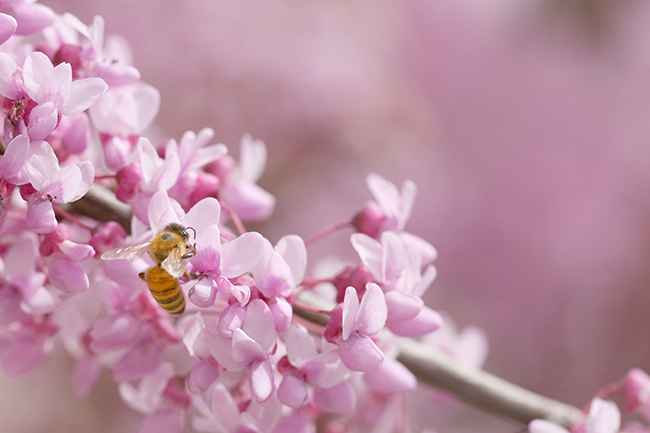

With the proper care you can not only add a flowery showpiece tree to your home or business, but also help local pollinators such as the honey bee
With the proper care, eastern redbuds can add much beauty to your landscape with their showy flowers and live for up to 25 years. The following tips will help you provide effective eastern redbud tree care:
- Planting: Eastern redbuds should be planted early in the spring. They do best in well-drained soil in areas with partial shade. When planting your eastern redbud, dig a hole that is three times wider than the root ball and just deep enough so that the top of the ball is even with the ground. Make sure the tree is straight as you fill the hole with native soil.
- Watering: Eastern redbuds have moderate tolerance to drought conditions, but they still need to be watered. You should water newly planted trees thoroughly once they are put in the ground and make sure the soil is moist while the tree is growing. Even moistness of the soil should be adequate for established trees. Redbud trees that are planted in full sun will need to be watered more regularly.
- Mulching: You can help the soil retain an adequate amount of moisture and nutrients for your eastern redbud by applying a 3-inch layer of mulch that extends to the drip line. Make sure the mulch is not touching the trunk.
- Fertilization: Applying a complete granular fertilizer early in the spring should provide enough nutrients for the season. Make sure you spread the fertilizer evenly over the root zone. If your tree is affected by cankers, you will need to apply slow release fertilizer at 6-week intervals.
- Pruning: The branches of eastern redbuds grow in zigzag patterns, making it important to prune them to maintain their shape. You should prune eastern redbuds to shape them in the early summer once they have finished blooming to remove large low branches and branches that cross into each other. In the late fall, prune the tree to remove dead or diseases branches. Several of the diseases and pests that affect eastern redbud trees can be treated with effective pruning. If you do not feel comfortable doing this yourself, you can call a professional arborist to handle the tree trimming.
Professional Tree Care for Eastern Redbud Trees from Hendricksen Tree Care

Contact Hendricksen Tree Care to see if an Eastern Redbud tree would be a good fit for your property today or if you need tree care maintenance of your existing trees!
The vibrant colors of the flowers and relatively easy maintenance make eastern redbuds a highly desirable ornamental tree for home landscapes. The early blooming flowers also attract wildlife such as butterflies and songbirds. It is important to ensure that your eastern redbuds are properly watered, fertilized, and pruned so that they can bloom fully and better resist pests and diseases. Working with our tree service professionals at Hendricksen Tree Care can also help ensure that your trees are properly cared for.
Hendricksen Tree Care is accredited by the Tree Care Industry Association (TCIA) with ISA certified arborists who can provide complete tree care services for all types of trees in the Chicago area. Our tree care services include fertilization, tree pruning, and tree treatment and diagnosis of pest infestations and diseases. You can trust our arborists to ensure that your eastern redbud trees get the care they need throughout the season to remain healthy and bloom fully. Hendricksen Tree Care services homes and commercial properties in Arlington Heights, Winnetka, Wilmette, Park Ridge, Northbrook, Lake Zurich, Lake Forest, Libertyville, Glenview, and the surrounding north and northwest Chicago suburbs.